Your cart is empty
Free shipping on all US orders


Free shipping on all orders
It doesn't take a rocket scientist to realize that we all aren't built the same way. While it's nice to think that we're all born equal and have the same inherent potential, that just isn't true.
At least, when it comes to our physical and metabolic characteristics. Some people are born having won the absolute genetic lottery, while others... not so much.
Nevertheless, there's no reason to cry over spoiled milk. Yes, you may be built differently from what you envision your ideal body type to be, but the good news is that you can still harness, and in some cases, exceed what you might believe you are limited to.
In this blog, we discuss what the different somatotypes are, along with the best diet and training strategies to improve your health and body composition.
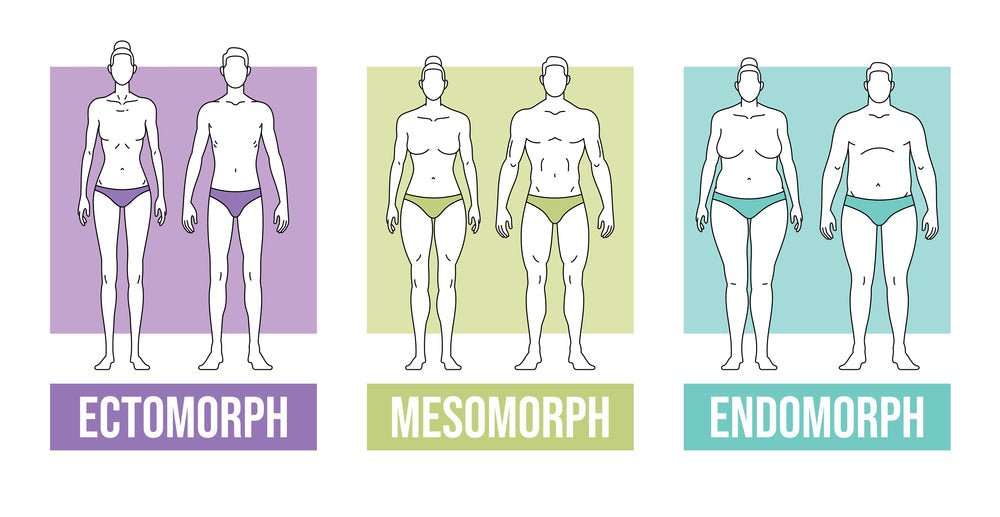
Your somatotype is just a fancy phrase to describe your body type.
Somatotypes are a system of classifying the human body according to its structure, shape, and growth patterns.
First proposed by American psychoanalyst William Herbert Sheldon in 1940, somatotypes look at the development potential of an individual and ask how close they might come to an optimal physical or psychological balance between three main elements: endomorphy (round, heavy-set features), mesomorphy (a slightly leaner form with some muscularity) and ectomorphy (flexible, long bones).

Each individual is said to have varying amounts of each type, which form a distinct overall body shape. Interestingly, despite the different proportions and combinations of the three somatotypes - 18 in total - most people tend to fit within one or two categories that remain constant throughout their life.
As such, somatotyping provides a useful insight into someone's physical build but also offers a unique biological blueprint from which we can understand more about our genetic heritage. Somatotypes may also explain challenges we may encounter in relation to our diet and fitness goals.
By understanding our own somatotype more clearly, we can adjust our lifestyle plans accordingly for greater well-being.
As briefly mentioned above, humans are broadly classified into one of three primary somatotypes, although most people will actually be a combination of two.
Not sure which class you fall into? Let's check them out below.
Ectomorphs are often referred to as “hard gainers” because they find it difficult to gain and maintain muscle. Typically, ectomorphs have a much longer, thinner build with narrow joints, small bones, and delicate features. This body type usually has a fast metabolism, making it difficult to gain weight or increase muscle mass.
Hyperactivity levels are typically high in ectomorphs and so they tend to enjoy more endurance-type activities such as running and swimming, rather than weights and power sports. Because of their relatively low amounts of body fat and muscle mass, ectomorphs are usually better adapted for aerobic activities with require submaximal power output. They naturally gravitate towards diets that are high in carbs for energy but can benefit from healthy fats as well as protein-rich meals to help them reach their goals faster.
Endomorphs are those who have a rounder body type, typically characterized by higher body fat and more of an inactive lifestyle. Endomorphs generally have a larger bone structure than other body types and tend to be inherently strong and muscular with little additional effort. They often have shorter limbs and thicker waists, as well as wide hips that can make aerobic activities more challenging for them. Of course, there is nothing wrong with being an endomorph; one's body type does not make them any less capable than the next person, it simply means that one must tailor their fitness program according to their individual needs. Endomorphs often respond best to higher-intensity workouts such as weightlifting, HIIT training, and cardio intervals coupled with a balanced nutrition plan that cuts back on sugar, carbs, and saturated fats while meaningfully increasing lean protein consumption. With this strategy in place, endomorphs can still build muscle and burn fat just like any other body type.
Mesomorphs are characterized by having a well-defined, symmetrical body structure, with broad shoulders and a narrow waist. With this body type comes natural strength, allowing mesomorphs to excel in various types of physical activity. Muscular development is generally easier for mesomorphs compared to people of other body types; they tend to gain muscle faster and can adjust to exercises quickly. They often have good posture, particularly when they focus on core strengthening exercises such as pilates or yoga.
With diligent training and proper nutrition, mesomorphs can achieve leanness while still holding onto muscle mass - a feat that may prove harder for those who fall into different categories such as ectomorphs or endomorphs. Mesomorphs are also blessed with naturally high levels of energy that allows them to be more active than others, which in turn helps them maintain their muscular physique. Overall, the mesomorphic body type offers distinct advantages for those looking to build strength and sculpt the perfect body shape!
An ectomorph diet is a meal plan designed to provide the essential nutrition and energy required by those with an ectomorph body type. For someone with an ectomorphic physique, this means having a diet that is high in both protein and carbohydrates and contains sufficient amounts of healthy fats.
A typical ectomorph diet emphasizes lean meats, legumes, complex carbohydrates (like whole grains and quinoa), fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and healthy oils such as olive oil or avocado oil. Additionally, plenty of water should be consumed on an ectomorph diet as it helps to stay hydrated and invigorated throughout the day. The goal of the ectomorph diet is to strike a balance between all nutrients while still providing enough calories for sustained energy; thus calorie counting isn't always necessary.
To achieve muscle gain, frequent meals if appetite persists, or fewer larger meals that are abundant in calories is advised.
Ectomorphs have fast metabolisms and a naturally-lean body type. For these people, developing muscle mass can be challenging as they are often unable to put on weight quickly. Given their unique physiology, ectomorphs should focus on workouts that emphasize building strength while limiting calorie expenditure. High-intensity interval training can be especially beneficial to ectomorphs because it combines short bursts of high exertion with ample recovery periods in between, allowing the body time to recover while still getting an excellent workout.
Cardio training might also be discouraged, but can also be beneficial in short intervals to support and maintain cardiovascular health.
Ectomorphs should also focus on progressive overload; the gradual increase of weight, sets, and reps over time. This is the best way for ectomorphs to gain strength and muscle mass while getting the most out of their workouts. With proper dieting and training, ectomorphs can achieve the body they desire.
An endomorph is a body type characterized by a rounder physique, a soft and fleshy abdominal area, short arms and legs, and the inability to quickly gain fat and gain muscle. Fat loss is also more difficult to achieve than for the other body types.
When designing an appropriate diet for an endomorph, there are several key factors to consider.
Firstly, although carbohydrates provide energy and help keep hunger at bay throughout the day, they should be limited in order to reduce weight gain.
The focus should instead be on higher-fiber foods such as vegetables and fruits that are fiber-rich and high in micronutrients. Second, rather than having one or two large meals during the day, it might be beneficial for endomorphs to create a timeline of smaller meals consumed regularly throughout the day so as to prevent shifts in blood sugar or dips in energy levels that can trigger cravings.
Finally, increasing protein consumption helps to maintain lean muscle mass while also helping to increase metabolism. This means that lean sources of protein -such as chicken breast or fish- should be prioritized over processed proteins like deli meat or pre-packaged burgers.
Be sure to supplement with a high-quality micronutrient supplement in order to compensate for possible nutritional deficiencies that occur from high-frequency training.
If you're an endomorph, finding the ideal exercise and workout routine can seem daunting. Luckily, there are a few basic principles to keep in mind that will help you tailor your activity to your endomorph body type.
Firstly, it is important to focus on strength training exercises. Endomorphs tend to accumulate fat more quickly than other body types, so regular weightlifting can help with body recomposition.
Cardio is also a necessity and should be performed several times a week. This can be done through running, cycling, swimming, or any other type of activity that increases the heart rate and increases caloric expenditure.
Finally, interval training is an excellent way to keep your workouts interesting and engaging while still getting all the benefits of cardio. Interval training involves alternating short bursts of high-intensity exercise with periods of low-intensity rest. This type of workout is particularly well-suited for endomorphs as it helps to maximize calorie expenditure while still allowing for shorter work durations.
This is helpful since this body type might find themselves training more rigorously than other somatotypes in order to achieve a physique they desire.
Mesomorph body types have a broad frame, strong muscle definition, and a tendency to gain fat evenly throughout their body. For mesomorphs, the ideal diet should focus on getting adequate nutrition while maintaining lean muscle mass. This can be achieved by eating plenty of lean proteins like poultry, fish, beans, and legumes, as well as high-fiber carbohydrates such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and nuts.
To promote healthy weight loss and muscle maintenance, it's important to keep processed foods and refined sugars to a minimum. The caloric intake for mesomorphs should also be adjusted depending on activity levels - limiting calories consumed when exercise is light or absent and increasing calorie intake when regular exercise is underway.
Finally, mesomorphs benefit from getting an adequate amount of daily protein - with meals providing 20-40 grams of protein each - to help keep protein synthesis high and support maximum performance in the gym.
Supplements that help increase workout performance, such as creatine and ATP can speed up the accrual of lean muscle mass and can be very helpful to the mesomorph.
If you are a mesomorph, you may be well-suited to athletic training routines such as weightlifting, HIIT workouts, and cardio sessions. Weightlifting can help to build your strength and fitness levels while improving athleticism.
Meanwhile, HIIT workouts have been proven to boost metabolism, helping reduce body fat and give you more muscle definition.
Of course, cardiovascular exercises are also important for maintaining good cardiovascular health and aiding recovery between heavier exertions. It's best to mix high-intensity aerobic activities with low-impact activities such as walking or cycling to avoid over-fatigue of joints.
Mesomorphs find it easier than the other body types to achieve their body goals, however, it is still important to maintain a regular and balanced exercise routine in order to sustain results.
Remember how we mentioned that humans are never only one body type? Most people are a blend of two somatotypes, as indicated below:
Thin frames with some athletic ability, classified as having lean muscle mass.
Gains muscle fairly easily, but also carries a propensity to store fat.
Sometimes referred to as skinny fat, this body type is thin but can also store fat easily.
Interestingly, you can elicit changes to your somatotype over an extended period of time, although it remains to be seen if these changes are permanent for the life of the person.
This is especially true in the sport of bodybuilding, where competitors strive to improve their muscle definition and body composition by adhering to a strict diet and exercise routine.
It is important to remember that somatotype is determined genetically, so it can be difficult - if not impossible - for someone to completely change their body type.
With the right diet and exercise plan, however, you can achieve the body you desire while adhering to your individual limitations.
It is also important to note that it may take months or even years before results become visible, so patience and dedication are key.
The famous bodybuilder and former Mr. Olympia winner Jay Cutler is a good example of an endomorph who has defied his somatotype by staying lean all year round and carrying an immense amount of muscle mass in the process.
It is, however very likely that should he discontinue training that his body would revert to the way it was before.
While you might have preferred to have a different body type combination than what you currently have, the good news is that hard work can actually emerge victorious over genetics.
By carefully crafting a diet and exercise routine tailored to your somatotype, you can achieve better body composition and improved health.
Remember that consistency is key, as it takes months or even years of dedication before visible results are seen.
Also, don’t be discouraged if you feel like you aren’t progressing as quickly as you’d like — it takes time and effort to make meaningful changes.