Your cart is empty
Free shipping on all US orders


Free shipping on all orders
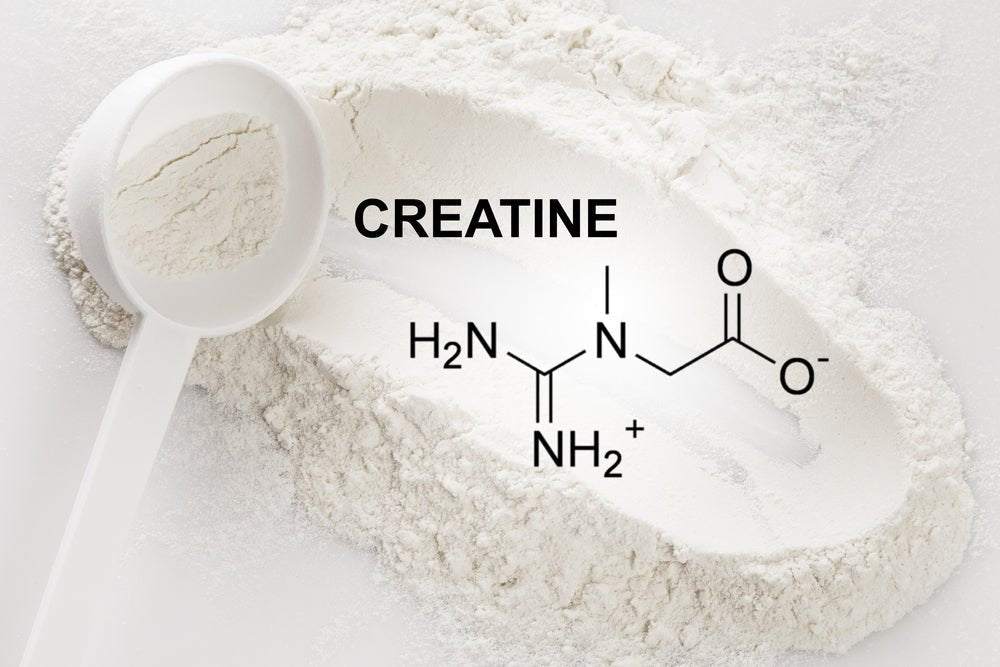
Creatine is the most studied supplement of all time. You know about it, your grandpa knew about it, and the buff pitbull from next door (probably) knows about it.
Jokes aside, there isn’t much left to guesswork when it comes to its usage for muscle and strength. But what many people don’t realize is the fact that there is an entire world of other benefits out there that creatine can be utilized for as well.
In this blog post, we’re going to be exploring some of the not-so-well-known exploits of the legendary creatine that might be worth some consideration.
You likely know of creatine as the go-to supplement for gym enthusiasts, aiding in muscle growth and strength gains. But did you know its benefits extend far beyond physical performance? Yes, recent research suggests creatine may play a significant role in neurological health, offering potential protection against debilitating neurodegenerative conditions like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's disease.
So how does this work? Your brain, like your muscles, requires a significant amount of energy to function optimally. Creatine helps to ensure that brain cells have a readily available energy supply by increasing phosphocreatine stores.
This boost in energy reserves can enhance cognitive function, memory, and overall brain health. Essentially, it provides your brain with the fuel it needs to operate at peak performance.
When it comes to neurodegenerative diseases, the research is particularly compelling. Conditions like Parkinson's and Alzheimer's are characterized by the progressive loss of brain cells and their function. Creatine shows promise in potentially slowing the progression of Parkinson's disease by also protecting brain cells from damage and improving motor function. This could translate to a better quality of life and independence for individuals living with the condition.
Similarly, studies suggest creatine may help manage or at least mitigate symptoms of Alzheimer's disease by boosting memory and cognitive performance, offering hope for maintaining cognitive abilities for a longer period.
While further research is definitely needed to fully understand creatine's impact on neurological health, the existing evidence is promising. It suggests that this readily available and safe supplement could play a key role in brain health maintenance and potentially contribute in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases.
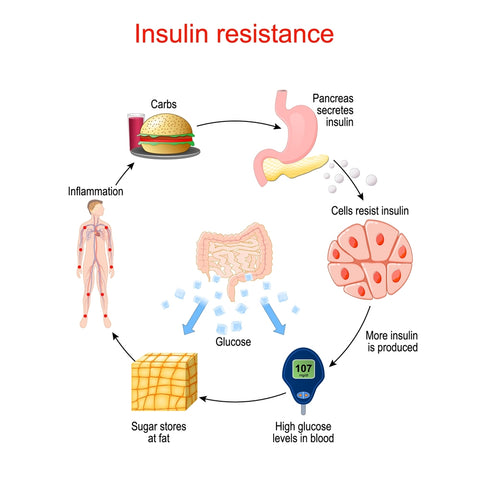
Creatine has been shown to have a positive impact on glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity, making it a potential therapeutic agent for individuals with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes.
One of the ways creatine enhances glucose tolerance is by increasing the expression and activity of glucose transporter proteins, particularly GLUT4, in skeletal muscle cells. GLUT4 is responsible for the uptake of glucose from the bloodstream into muscle cells, where it can be used for energy production or stored as glycogen for longer-term needs.
By upregulating GLUT4, creatine facilitates more efficient glucose uptake, thereby lowering blood glucose levels and improving overall glucose tolerance.
In addition to its effects on glucose transport, creatine has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity. Insulin plays a critical role in regulating glucose metabolism by stimulating glucose uptake in peripheral tissues and suppressing glucose production in the liver.
In states of insulin resistance, such as in type 2 diabetes, the body's tissues become less responsive to insulin, leading to impaired glucose uptake and elevated blood glucose levels. Creatine has been found to improve insulin sensitivity by enhancing the activation of downstream signaling pathways involved in insulin action, such as the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (Akt) pathways.
By potentiating insulin signaling, creatine helps to overcome insulin resistance and improve glucose utilization in insulin-sensitive tissues, such as skeletal muscle and adipose tissue.
Its role in energy metabolism may indirectly contribute to improved glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Creatine is known to enhance mitochondrial function and ATP production, which can lead to a more efficient utilization of glucose for energy production.
By promoting the oxidative metabolism of glucose in skeletal muscle, creatine may reduce the accumulation of toxic glucose metabolites and improve overall glucose homeostasis.
The anti-inflammatory properties of creatine may also lend a hand in enhancing insulin sensitivity. Chronic low-grade inflammation has been linked to the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. By reducing inflammation, creatine may help to mitigate the negative impact of inflammatory cytokines on insulin signaling and glucose metabolism.
Recent research suggests that creatine may also play a role in lowering homocysteine levels, which could ultimately reduce the risk of heart disease. Homocysteine is an amino acid that, when present in high levels, has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular problems, including heart attacks and strokes.
The mechanism by which creatine may lower homocysteine levels is related to its involvement in the methylation process. Methylation is a necessary biochemical process that involves the transfer of a methyl group (CH3) from one molecule to another.
In the case of homocysteine, methylation is essential for converting it back to methionine, a harmless amino acid.
Creatine plays a role in this process by donating a methyl group to guanidinoacetate, forming creatine. This reaction is catalyzed by the enzyme guanidinoacetate methyltransferase (GAMT), which uses S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) as the methyl donor.
By promoting the formation of creatine through the GAMT reaction, the body can regenerate SAM more efficiently. SAM is an important component in the methylation of homocysteine, as it donates its methyl group to homocysteine, converting it back to methionine.
When creatine levels are sufficient, the GAMT reaction can proceed smoothly, ensuring an adequate supply of SAM for homocysteine methylation. This, in turn, helps to maintain lower levels of homocysteine in the blood, reducing the risk of heart complications.
Creatine supplementation has been shown to increase the activity of the enzyme methionine synthase, which is directly responsible for the methylation of homocysteine to methionine. By enhancing the activity of this enzyme, creatine may further contribute to the efficient removal of homocysteine from the bloodstream.
By supporting the methylation process and promoting the conversion of homocysteine back to methionine, creatine could potentially offer a complementary approach to reducing the risk of heart disease.
Your blood vessels play a vital role in delivering oxygen and nutrients throughout your body, and maintaining their health is crucial for overall well-being. This is where creatine steps in, offering the potential for enhancing blood vessel function and reducing arterial stiffness.
Arterial stiffness is a key indicator of cardiovascular health. It signifies a loss of elasticity in your arteries, making them less efficient at accommodating blood flow. This can lead to an increased risk of high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke.
However, creatine supplementation may offer a solution. Studies indicate that creatine can promote the production of nitric oxide, a molecule that acts as a vasodilator, relaxing and widening blood vessels.
This improved blood flow not only benefits your muscles during exercise but also contributes to overall cardiovascular health, ensuring efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients to all parts of your body.
The advantages of improved vascular function extend beyond the immediate cardiovascular system. When your organs and tissues receive optimal blood flow, they are better equipped to function efficiently.
This can have positive effects on various aspects of your health. For instance, efficient oxygen and nutrient delivery to your muscles can help enhance your endurance and stamina during exercise.
Picture this: you're exercising in hot and humid conditions, pushing your body to its limits. As the temperature rises, you start to feel the heat taking its toll on your performance. But what if there was a way to improve your body's ability to regulate its temperature during exercise in hot environments? You guessed right; creatine may just be your secret weapon for beating the heat.
You see when you exercise in hot conditions, your body has to work harder to maintain a stable core temperature. This can lead to increased fatigue, reduced performance, and even heat-related illnesses.

However, research has shown that creatine supplementation can help improve your body's thermoregulation during exercise in the heat.
So, how does it work its magic? When you supplement with creatine, you increase your body's stores of phosphocreatine, a high-energy compound that helps produce ATP, the energy currency of your cells. This extra energy can help your body maintain optimal function, even under the stress of heat.
Studies have found that creatine supplementation can help reduce your body's core temperature during exercise in the heat, allowing you to perform better and longer. This is because creatine helps your body produce more ATP, which in turn supports your muscles' ability to contract and generate force. With more energy available, your body can work more efficiently, even in challenging conditions.
But the benefits on thermoregulation don't stop there. Creatine can also improve your body's ability to sweat, which is a crucial mechanism for cooling your body during exercise. By enhancing your sweating response, creatine can help you dissipate heat more effectively, reducing your risk of heat-related illnesses like heat exhaustion and heat stroke.
Creatine supplementation has also been found to increase your body's plasma volume, which is the liquid portion of your blood. A higher plasma volume means that your body can more efficiently transport heat from your core to your skin, where it can be released through sweating. This improved circulation can help you maintain a more stable core temperature, even when the heat is on.
In this hectic world, sleep deprivation has become an all-too-common issue, affecting millions of people worldwide. The consequences of not getting enough sleep can be severe, ranging from decreased cognitive function and mood disturbances to impaired physical performance.
Recent research suggests that creatine supplementation may help combat the cognitive and physical impairments associated with sleep deprivation.
One of the primary ways creatine helps reduce the symptoms of sleep deprivation is by supporting brain function. When you're sleep-deprived, your brain's energy reserves become depleted, leading to decreased cognitive performance, difficulty concentrating, and impaired decision-making.
Creatine, however, has been shown to enhance brain energy metabolism by increasing the availability of ATP. By providing your brain with the energy it needs to function optimally, creatine may help you maintain better cognitive performance, even when you're running on little sleep.
In addition to its cognitive benefits, creatine may also help reduce the physical symptoms of sleep deprivation. When you're sleep-deprived, your body's ability to perform physical tasks can be significantly impaired, leading to decreased strength, power, and endurance.
However, research has shown that supplementation can help improve physical performance in sleep-deprived individuals.
Sleep deprivation can lead to increased oxidative stress and inflammation in the brain, which can contribute to the development of neurodegenerative disorders like Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. By combating oxidative stress and inflammation, creatine may help preserve brain health and reduce the long-term consequences of sleep deprivation.
Keep in mind, however, that while creatine is not a substitute for a good night's sleep, it may be a valuable tool for those who occasionally find themselves in situations where adequate sleep is not possible.
If you're a shift worker, a new parent, or simply someone who struggles with sleep from time to time, creatine supplementation may help you better cope with the symptoms of sleep deprivation. Be sure to prioritize healthy sleep habits whenever possible, and if you need a little help, try non-habit forming Dreamzzz.
Creatine has shown potential in reducing the risk of certain cancers through various mechanisms. One of the primary mechanisms by which creatine may help prevent cancer is through its potent antioxidant capacity.
Creatine directly scavenges free radicals and enhances the activity of antioxidant enzymes, protecting cells from oxidative damage, which is a significant contributor to cancer development. By maintaining cellular integrity and preventing mutations that could lead to uncontrolled cell growth, creatine's antioxidant action plays a crucial role in cancer prevention.
Creatine's involvement in energy metabolism may indirectly influence cancer cell behavior, too. By promoting efficient mitochondrial function and ATP production, creatine could potentially shift cancer cell metabolism away from the glycolytic Warburg effect, which is characteristic of many cancer cells, towards a less aggressive phenotype that relies on oxidative phosphorylation.
This metabolic shift might slow down tumor growth and improve the effectiveness of cancer treatments by making cancer cells more susceptible to therapeutic interventions.
In addition to its metabolic effects, creatine interacts with various cell signaling pathways involved in cancer cell growth and survival. Research indicates that creatine can encourage apoptosis, the programmed self-destruction of cells, thereby eliminating abnormal cells and reducing tumor burden.
This is particularly important in cancer prevention, as apoptosis helps to remove cells with potentially cancerous mutations before they can proliferate and form tumors. It may even influence cell cycle regulation, preventing uncontrolled proliferation, which is a hallmark of cancer. By modulating signaling pathways that control cell division, creatine could help maintain normal cell growth and reduce the risk of cancer development.
Beyond its direct actions on cancer cells, creatine's anti-inflammatory properties may indirectly reduce cancer risk by mitigating chronic inflammation. Chronic inflammation has been identified as a contributing factor to cancer development, as it creates a favorable environment for tumor growth and promotes the accumulation of DNA damage. By reducing inflammation, creatine may help to prevent the initiation and progression of cancer.
While more research is needed to fully understand the extent of creatine's anti-cancer effects, the current evidence suggests that it may be a valuable supportive agent in cancer prevention and treatment strategies.
Sarcopenia is a significant concern for the aging population, as it can lead to decreased mobility, increased risk of falls, and an overall decline in the quality of life. Similarly, muscle loss during immobilization, such as that experienced during hospitalization or injury recovery, can have detrimental effects on an individual's health and functional capacity.

One of the primary mechanisms by which creatine may help reduce the risk of sarcopenia and muscle loss during immobilization is through its ability to enhance muscle protein synthesis. Creatine has been shown to increase the expression of insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), a key regulator of muscle growth and repair. By stimulating IGF-1 production, creatine can promote the synthesis of new muscle proteins, helping to maintain or even increase muscle mass in older adults and those experiencing immobilization.
In addition to its effects on muscle protein synthesis, creatine may also help preserve muscle mass by reducing muscle protein breakdown. During periods of inactivity or reduced muscle use, the body may break down muscle proteins to use as energy or to support other physiological processes. The body does not want to hold on to extra muscle mass, and in the absence of stimuli that allows retention, it is actively lost.
Creatine supplementation has been shown to attenuate this muscle protein breakdown, potentially by improving energy availability within the muscle cells and reducing the need for protein catabolism.
Creatine supplementation may also have beneficial effects on muscle endurance and recovery, which are important factors in maintaining muscle mass and function in older adults.
By enhancing muscle energy stores and reducing fatigue, creatine can allow individuals to engage in longer and more intense physical activities, providing a greater stimulus for muscle preservation. Additionally, creatine's role in reducing inflammation and oxidative stress may support muscle recovery and regeneration, further contributing to the prevention of muscle loss.
Clinical studies have provided evidence for the effectiveness of creatine supplementation in reducing the risk of sarcopenia and age-associated muscle loss.
Older adults who supplemented with creatine in combination with resistance training have shown greater improvements in muscle mass, strength, and functional performance compared to those engaging in resistance training alone.
Similarly, creatine supplementation has been found to attenuate muscle loss and strength decline in individuals undergoing periods of immobilization, such as during leg immobilization or periods of extended bed rest.
There are so many reasons to use creatine- even if you’ve never worked out a day in your life. It is truly, a miracle supplement. If you’ve never used it before, it’s always a good idea to consult your health care provider before starting to ensure that all systems are go