Your cart is empty
Free shipping on all US orders


Free shipping on all orders
If you've ever suffered from a sleep disorder, then you know how desperate things can get.
Everything positive in your life is affected; from your physical strength to your mental wellbeing and energy levels. It's not a pretty sight.
Not surprisingly, sleep medicine is in high demand, even if it comes at high risk.
Enter melatonin; the body's natural fix to your sleep problem. Can it help save the day? Read on below to see how melatonin could help you, and quite likely save you from a lot of heartache down the road.
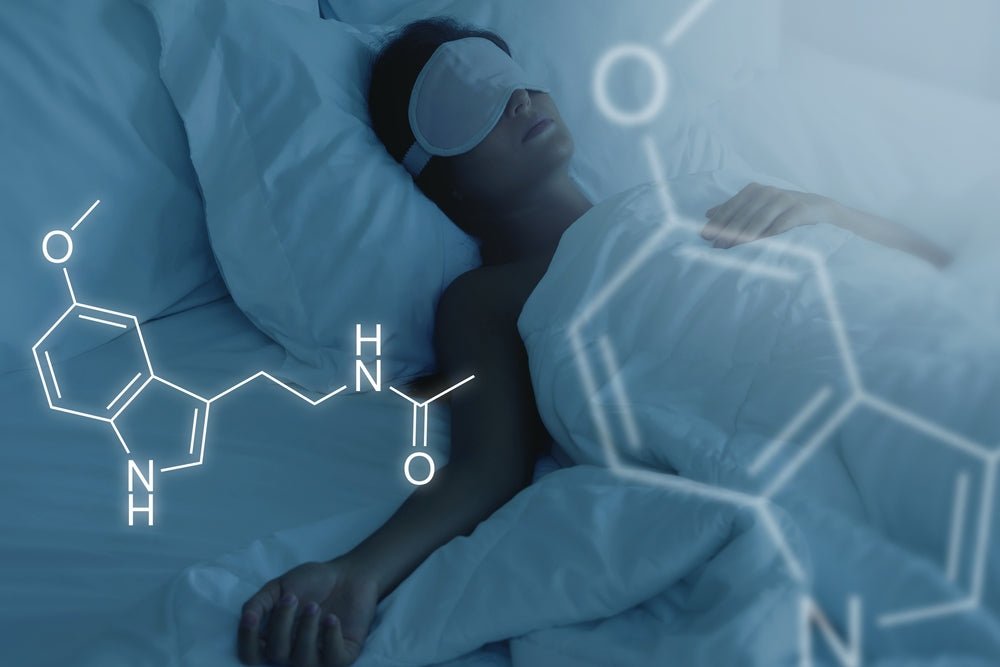
Melatonin is a hormone that is naturally produced by the body's pineal gland, located in the brain. It plays an important role in regulating sleep and wake cycles, as well as other physiological functions. Melatonin levels rise in the evening and decrease in the morning, which helps promote sleep at night and wakefulness during the day.

Melatonin is a hormone classified as a chronobiotic agent, which means that it helps regulate circadian rhythms and the body's internal clock.
Specifically, melatonin is a derivative of the neurotransmitter serotonin and is responsible for several important aspects of health.
However, melatonin secretion tends to diminish with advancing age, leading many people to wonder if supplemental melatonin used as a sleep aid is a good choice.
You will be pleased to hear that the use of exogenous melatonin is effective, not only for temporary sleep disturbance but also for many other things.
Melatonin plays a key role in regulating the body's sleep wake cycle, which is controlled by the circadian rhythm. The circadian rhythm is the body's internal clock, which tells us when it is time to sleep and wake up.

Melatonin production is closely linked to this circadian rhythm and is controlled by a complex feedback loop involving light and dark signals.
Melatonin production is highest at night and lowest during the day. The production of melatonin is triggered by darkness and inhibited by light.
In the evening, when light levels decrease, the pineal gland in the brain begins to produce melatonin, which signals to the body that it is time to sleep. As melatonin levels rise, the body's temperature drops, and heart rate and breathing slow down, preparing the body for sleep.
During the night, melatonin levels remain high, promoting deep, restorative sleep. In the morning, when light levels increase, melatonin production decreases, signaling the body to wake up. As the body becomes more alert, the production of other hormones, such as cortisol, increases, helping to promote wakefulness and energy.
This is why one of the primary uses of melatonin is for circadian rhythm sleep disorders.
Melatonin is best known for its ability to help you get restful sleep, but how does it do this exactly?
It is believed that melatonin promotes sleep by interacting with various receptors in the brain that regulate the sleep-wake cycle.
Melatonin primarily binds to two receptors in the brain: MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptor subtypes. These receptors are found in several areas of the brain, including the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) and the hypothalamus, which are involved in the regulation of the aforementioned circadian rhythm.
When melatonin binds to these receptors, it triggers a series of events that promote sleep. One of the primary mechanisms by which melatonin promotes sleep is by reducing the activity of neurons in the SCN.
This helps to suppress the production of stimulating hormones such as cortisol and increase the production of sleep-promoting hormones such as prolactin.
Melatonin also helps to initiate sleep onset by reducing body temperature, heart rate, and respiration rate. These changes help the body prepare for sleep by lowering its metabolic rate and conserving energy.
Additionally, melatonin promotes the production of the neurotransmitter GABA, which helps to calm the activity of neurons in the brain and promote relaxation. This helps to reduce anxiety and promote feelings of calmness, which are important for falling and staying asleep.
Do you dread the feeling of jet lag you get after a long flight? Jet lag occurs when the body's internal clock is disrupted by travel across different time zones, causing a mismatch between the body's internal clock and the external environment.

Melatonin can help to reset the body's internal clock and promote healthy sleep patterns. When taken at the appropriate time, melatonin can help to reduce the symptoms of jet lag, such as difficulty falling asleep at night and daytime fatigue.
The timing and dosage of melatonin are important factors in treating jet lag. It is recommended to take melatonin at the appropriate time in relation to the destination time zone, typically in the evening before bedtime. This helps to signal to the body that it is time to sleep and can help to reset the circadian rhythm.
Studies have shown that melatonin supplementation can be effective in reducing the symptoms of jet lag and improving sleep quality.
It may also be useful in helping people who do shift work to rapidly help their circadian rhythm adapt.
A little-known effect of melatonin is on helping to boost the immune system. Specifically, melatonin has been found to improve the function of T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells, which play a key role in fighting off infections and diseases.
One way that melatonin is believed to enhance immune cell activity is by increasing the production of cytokines, which are signaling molecules that help to activate immune cells. This can help to increase the overall effectiveness of the immune system and improve the body's ability to fight off infections.
In addition, melatonin has been found to regulate the inflammatory response in the body. By reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and increasing the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, melatonin can help to reduce inflammatory load throughout the body. This is important because chronic inflammation has been linked to several diseases, including heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
Melatonin also has antioxidant properties, which can help to protect against oxidative damage. Excessive oxidative damage occurs when there is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants in the body, which leads to damage to cells and tissues, sometimes resulting in premature aging. By acting as an antioxidant, melatonin can help to protect against this damage and promote overall health.
Melatonin may have a preventative effect on neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease by influencing various mechanisms in the body.
One of the main ways melatonin may help to prevent these diseases is by reducing oxidative stress in the brain. Although not the only factor in the development of these conditions, there is a strong correlation.

Melatonin has also been shown to inhibit the aggregation of the amyloid beta protein, which is a key component of the plaques that accumulate in the brains of Alzheimer's patients.
Another way that melatonin may help to prevent neurodegenerative diseases is by promoting neuroplasticity. Neuroplasticity is the brain's ability to adapt and change in response to new experiences (or stimuli). Melatonin has been shown to promote neuroplasticity by increasing the production of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), a protein that helps to promote the growth and survival of neurons.
Finally, melatonin may help to protect against excitotoxicity, a process where neurons are damaged or killed due to excessive stimulation by neurotransmitters.
Melatonin can help to protect against excitotoxicity by reducing the production of the neurotransmitter glutamate and increasing the production of the inhibitory (or calming) neurotransmitter GABA.
Here's another shocker: melatonin is actually pretty damn good when it comes to regulating blood pressure! By extension, melatonin can help to reduce hypertension and improve cardiovascular health.
Firstly, melatonin reduces the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, which is responsible for regulating blood pressure by increasing heart rate and constricting blood vessels.
By reducing the activity of the sympathetic nervous system, melatonin can help to relax blood vessels and lower blood pressure, which is a major win for your cardiovascular system.
Additionally, melatonin increases the production of nitric oxide, a natural vasodilator molecule that helps to relax blood vessels and improve blood flow.
With increased nitric oxide production, melatonin can help to lower blood pressure and promote better blood circulation, which is essential for overall health.
Melatonin also regulates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS), a hormonal system that constricts blood vessels and raises blood pressure.
By reducing the production of renin and angiotensin II, melatonin can help to lower blood pressure.
Then there's the fact that studies have found that melatonin supplementation can lead to a reduction in total cholesterol levels, an increase in HDL cholesterol levels (often referred to as "good" cholesterol), and reduced triglyceride levels in some cases.
This is very good when it comes to lowering your risk of experiencing an ischemic attack as the result of arteries blocked with atherosclerotic plaque deposits.
Last but not least, melatonin helps to improve sleep quality, which has been linked to a lowered risk of hypertension and other cardiovascular diseases. By improving sleep quality, melatonin can help to optimize blood pressure and promote a healthy heart.
Think jet lag is bad? Welcome to the SAD time. Luckily, melatonin can help manage seasonal affective disorder (SAD) and promote positive mood by its action on circadian rhythm and promoting healthy sleep patterns.
SAD is a type of depression that is linked to seasonal changes, typically occurring during the fall and winter months when there is less sunlight.
Melatonin plays a key role in regulating the body's circadian rhythm, which is the internal "clock" that controls the sleep wake cycle.
By taking melatonin supplements, individuals with SAD can help regulate their circadian rhythm, which can help to alleviate symptoms of depression and improve mood.
Poor sleep quality is linked to depression and other mood disorders, and individuals with SAD often experience disruptions in sleep patterns.
In addition, melatonin has been shown to have a positive effect on neurotransmitters such as serotonin and dopamine, which play a key role in regulating mood. By increasing the production of these neurotransmitters, melatonin can help to promote a positive mood and alleviate symptoms of depression and SAD.
Melatonin supports eye health in several ways, including protecting against blue light and promoting the regeneration of retinal cells.
Blue light is a type of high-energy visible light that can damage the retina and contribute to the premature development of age-related macular degeneration (AMD).

Melatonin helps to protect against blue light by acting as an antioxidant and reducing oxidative stress in the retina. Additionally, melatonin has been shown to inhibit the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the retina, which can help to further reduce inflammation and protect against AMD.
Melatonin also promotes the regeneration of retinal cells, which can help to maintain healthy vision. The retina is complex and is responsible for converting light into electrical signals that the brain can interpret as images.
Over time, the cells in the retina can become damaged or die, leading to vision loss. Melatonin can help to promote the regeneration of retinal cells, which may help to maintain healthy vision and prevent vision loss.
The sleep promoting properties of melatonin is also helpful here. Poor sleep quality has been linked to several eye conditions, including dry eye syndrome and glaucoma.
All in all, it does far more than you might have expected for the eyes.
The inability to conceive is a major pain point for millions of people around the world.
Melatonin, however, has been shown to have a positive effect on fertility in both men and women. It helps to regulate the production of important reproductive hormones, including luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), which play a key role in regulating the menstrual cycle and ovulation in women, and spermatogenesis (sperm production) in men.

Melatonin is also a potent antioxidant that can help to protect against oxidative stress, which may improve fertility by reducing damage to sperm and egg cells.
Melatonin can also help to improve egg viability in women undergoing fertility treatments and enhance sperm quality in men with fertility problems.
You can find a melatonin supplement available in various forms, including tablets, capsules, gummies, and liquids.
The recommended dose of melatonin varies depending on the reason for use and the individual's age and health status. Generally, a dose as low as 0.2 to 0.5 milligrams is sufficient for regulating sleep-wake cycles, while higher doses of 5 to 10 milligrams may be needed for treating certain sleep disorders, occasional sleeplessness, or refractive insomnia.
However, it's important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines on the supplement label or as recommended by a healthcare professional.
Our very own Dreamzzz is a natural sleep aid that contains melatonin and synergistic herbs to help you get the best possible rest, without the risk of prescription pills.
Melatonin ingestion is usually recommended 30 to 60 minutes before bedtime. It's important to take melatonin at the same time each day to help regulate sleep-wake cycles. It's also important to avoid taking melatonin with alcohol or other sedatives, as this can increase drowsiness and impair cognitive function.
Melatonin is generally considered safe when used in recommended doses for periods of time. However, as with any supplement or medication, there may be potential risks and adverse effects associated with melatonin use.
Some common side effects of melatonin include drowsiness, headache, dizziness, daytime sleepiness, and nausea. These side effects are typically mild and go away on their own. Additionally, some people may experience vivid dreams or nightmares when taking melatonin, although this is not considered a serious side effect.
Even long-term use of melatonin supplements is generally safe, although disruption of natural sleep-wake cycles is likely as your body grows dependent on the supplement.
Additionally, melatonin supplements may interact with certain medications, including blood thinners, blood pressure medications, and antidepressants.
It's important to talk to your healthcare provider before taking melatonin supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking other medications.
Taking a melatonin pill to help deal with a sleep disorder or sleep problem is not something to be ashamed of; in fact, melatonin is an absolutely effective dietary supplement for fixing a sleep cycle that is off track.
Plus, the slew of other helpful benefits really helps to put its utility in focus.
We would recommend you not “sleep” on this one! (pun intended)